Way back in 1952 i.e., almost with the inception of planning in India, the idea
was mooted to establish Agro-Economic Research Centre for each state to serve as
the catalyst of region specific agricultural transformation. It was one of the earliest
institutional efforts to propagate and interweave knowledge based farming to a specific
region.
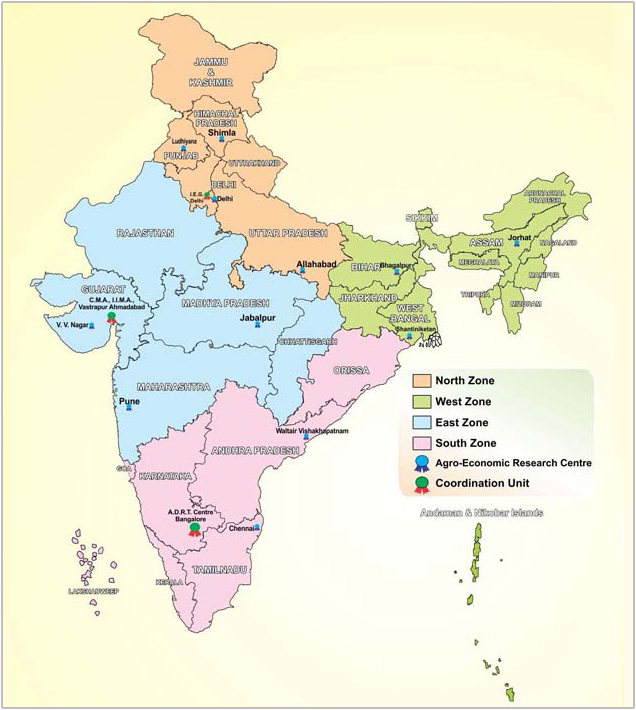
The year 1954 was a landmark in the history of agricultural economics in India as
in that year the Ministry of Food and Agriculture, Government of India, established
4 Agro- Economic Research Centres at Delhi, Pune, Chennai and Santiniketan. 2 more
centres were established in 1958, one at Jorhat (Assam) and another at Sehore (Madhya
Pradesh). In 1961 one more Agro Economic Research Centre was established at VallabhVidyaNagar.In
the later years three more centres were established at Allahabad, Waltair and Shimla
bringing the total number of centres in the country to 10. In 1966 two more centres
were established at Ludhiana and Bhagalpur. Thus, at present there are 12 AER Centres
functioning in the country in coordination of three ministries i.e. IEG New Delhi,
IIM Ahmadabad and ADRT, Bangalore.
The Agro Economic Research Centres are autonomous bodies. These function as separate
departments under the administrative and functional control of the university /
institute where these are located. These centres are totally financed by Government
of India through grant-in-aid.
Agro Economic Research Centre for central India (M.P. and Rajasthan) was established
at Sehore on 22nd December, 1958. In May, 1960 it was shifted from Sehore to Gwalior.
The jurisdiction of Gwalior centre was confined to Madhya Pradesh. With the establishment
of J. N. Krishi Vishwa Vidyalaya the administrative control of the Centre was transferred
to J.N.K.V.V. from 1st April, 1965.